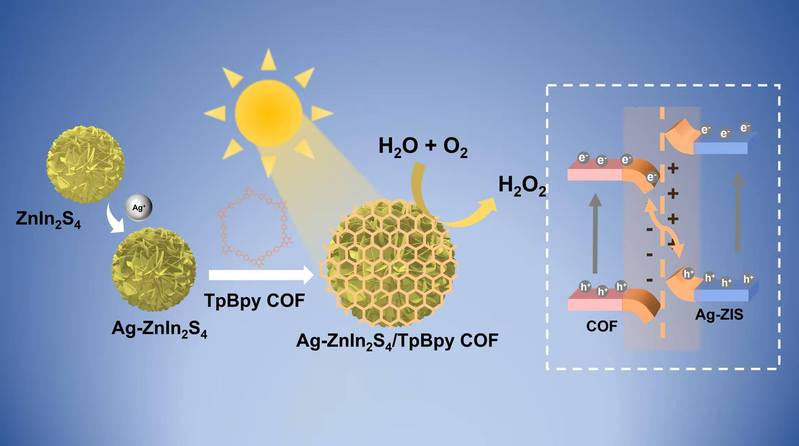
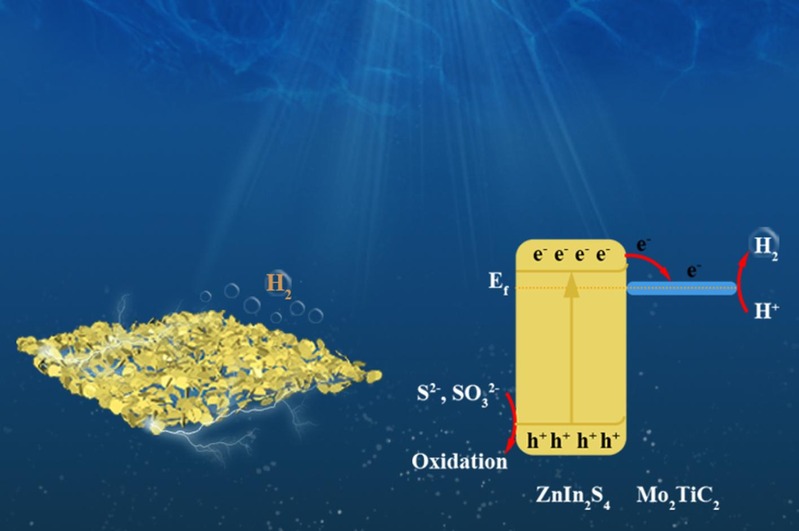
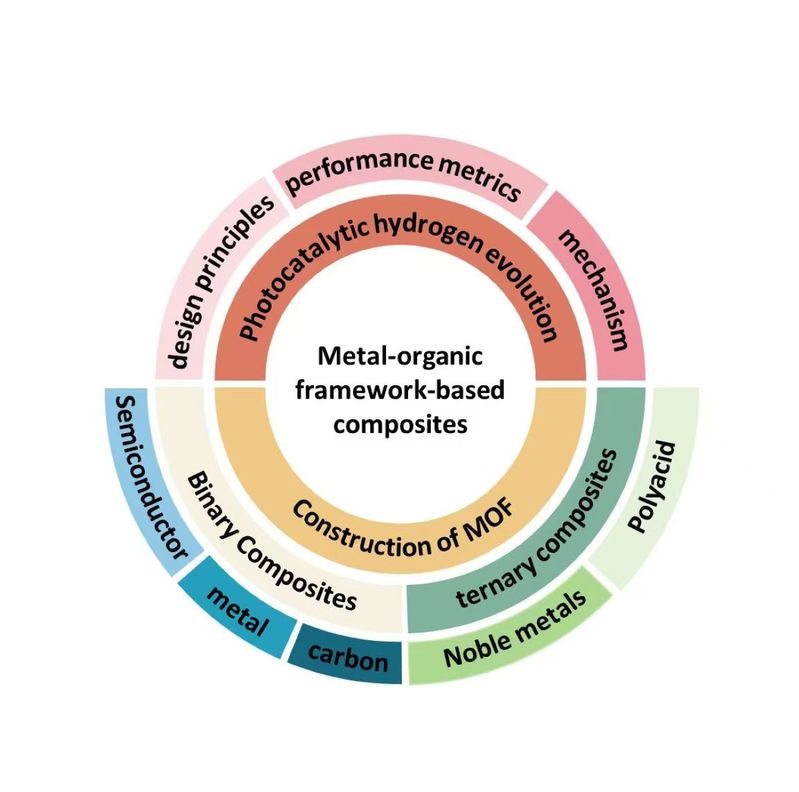
The development of metal–organic framework (MOF)-based composites for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution has garnered significant attention due to their tunable structures, high surface area, and abundant active sites. Recent advancements focus on enhancing light absorption, charge separation, and catalytic efficiency through strategies such as ligand functionalization, metal doping, heterojunction formation, and plasmonic coupling effects. For instance, modifications with Ir (III) complexes and Pt nanoparticles have significantly improved hydrogen evolution rates, while sandwich-structured MOF composites demonstrate optimized charge separation through tailored micro-environments and proton reduction efficiency. Additionally, integrating MOFs with semiconductors (e.g., CdS, g-C3N4) or plasmonic metals (e.g., Au) enhances visible-light responsiveness and stability. This review highlights key design principles, performance metrics, and mechanistic insights, providing a roadmap for future research in MOF-based photocatalysts for sustainable hydrogen production. Challenges such as long-term stability and scalable synthesis are also discussed to guide further innovations in this field.
 Wei-Lin Dai Group
Wei-Lin Dai Group